Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a serious health condition that affects millions of Americans. If left unchecked, it can lead to severe complications like heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and more. Fortunately, managing hypertension is possible with the right lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring. This article will discuss some essential tips for controlling it and maintaining cardiovascular health.
Understand What Hypertension Is
Hypertension occurs when the force of the blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is recorded with two numbers: systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number). A regular reading is usually around 120/80 mmHg. It is diagnosed when the systolic reading is 130 or higher, or the diastolic reading is 80 or higher.
Chronic hypertension can lead to complications in the heart, kidneys, and other vital organs. The risk of hypertension increases with age, a poor diet, lack of physical activity, obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and family history. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding your blood pressure numbers are the first steps toward managing this condition.
Maintain a Healthy Diet
Diet plays a critical role in managing high blood pressure. A heart-healthy diet can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is particularly effective for managing hypertension. This diet emphasizes:
- Fruits and vegetables: Aim to consume at least 4-5 servings of fruits and vegetables daily.
- Whole grains: Choose brown rice, oats, and whole-wheat bread.
- Lean proteins: Include lean protein sources like chicken, fish, beans, and legumes.
- Low-fat dairy: Opt for low-fat or fat-free milk, yogurt, and cheese.
- Nuts and seeds: Incorporate a variety of nuts and seeds for healthy fats and fiber.
Limiting the intake of sodium (salt) is essential for managing hypertension. The American Heart Association recommends consuming no more than 1,500 mg of sodium per day for people with blood pressure. Avoid processed foods, fast food, canned soups, and salty snacks, as they are typically high in sodium.
Another essential nutrient to monitor is potassium. Potassium helps balance the effects of sodium and can help lower blood pressure. Foods like bananas, sweet potatoes, spinach, and beans are excellent sources of potassium. Reducing your intake of alcohol and caffeine can also contribute to better blood pressure control.
Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity is one of the most effective ways to lower and control it . Regular exercise strengthens the heart, enabling it to pump blood more efficiently and reducing the pressure in the arteries. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity each week.
Some practical exercises for managing hypertension include:
- Walking: A brisk 30-minute walk most days of the week can help lower blood pressure.
- Jogging or running: Higher-intensity exercises like jogging can further improve cardiovascular health.
- Cycling: Whether indoors or outdoors, cycling is a great way to get your heart pumping.
- Swimming: This full-body workout enhances heart health and lowers blood pressure.
- Yoga: Relaxation exercises like yoga can reduce stress, which helps lower blood pressure.
Strength training can be beneficial in addition to aerobic exercise. Incorporating weight training two or more times per week helps improve muscle strength and overall metabolism. However, talking to your healthcare provider before starting a new exercise program is essential, especially if you have existing health concerns.
Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress is a known contributor to high blood pressure. When stressed, your body produces hormones like adrenaline that increase your heart rate and narrow blood vessels, causing a temporary spike in blood pressure. Over time, chronic stress can contribute to sustained hypertension.
Managing stress effectively is crucial for controlling blood pressure. Some strategies for reducing stress include:
- Deep breathing exercises: Taking deep, slow breaths can activate your body’s relaxation response and lower stress.
- Meditation: Mindfulness meditation can help you stay focused and calm in stressful situations.
- Progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and relaxing different muscle groups to relieve tension.
- Time management: By organizing your schedule, reducing the pressure of everyday tasks can help lower stress.
- Social support: Talking to friends or family can help alleviate stress and improve mood.
Physical activities like yoga and tai chi also reduce stress and promote relaxation. Regular practice can help lower both systolic and diastolic blood pressure over time.
Medication and Regular Monitoring
Sometimes, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to control high blood pressure. If this is the case for you, your healthcare provider may prescribe medication to help lower your blood pressure. There are several classes of antihypertensive drugs, including:
- Diuretics: Help reduce the amount of fluid in the blood vessels, lowering blood pressure.
- ACE inhibitors Block the hormone that narrows blood vessels, allowing them to relax and widen.
- Calcium channel blockers: Prevent calcium from entering heart and blood vessel cells, helping them relax.
- Beta-blockers: Reduce the workload on the heart by blocking stress hormones.
It’s essential to take your medications exactly as prescribed. Skipping doses or stopping medicines without your doctor’s approval can lead to uncontrolled hypertension and increase the risk of complications.
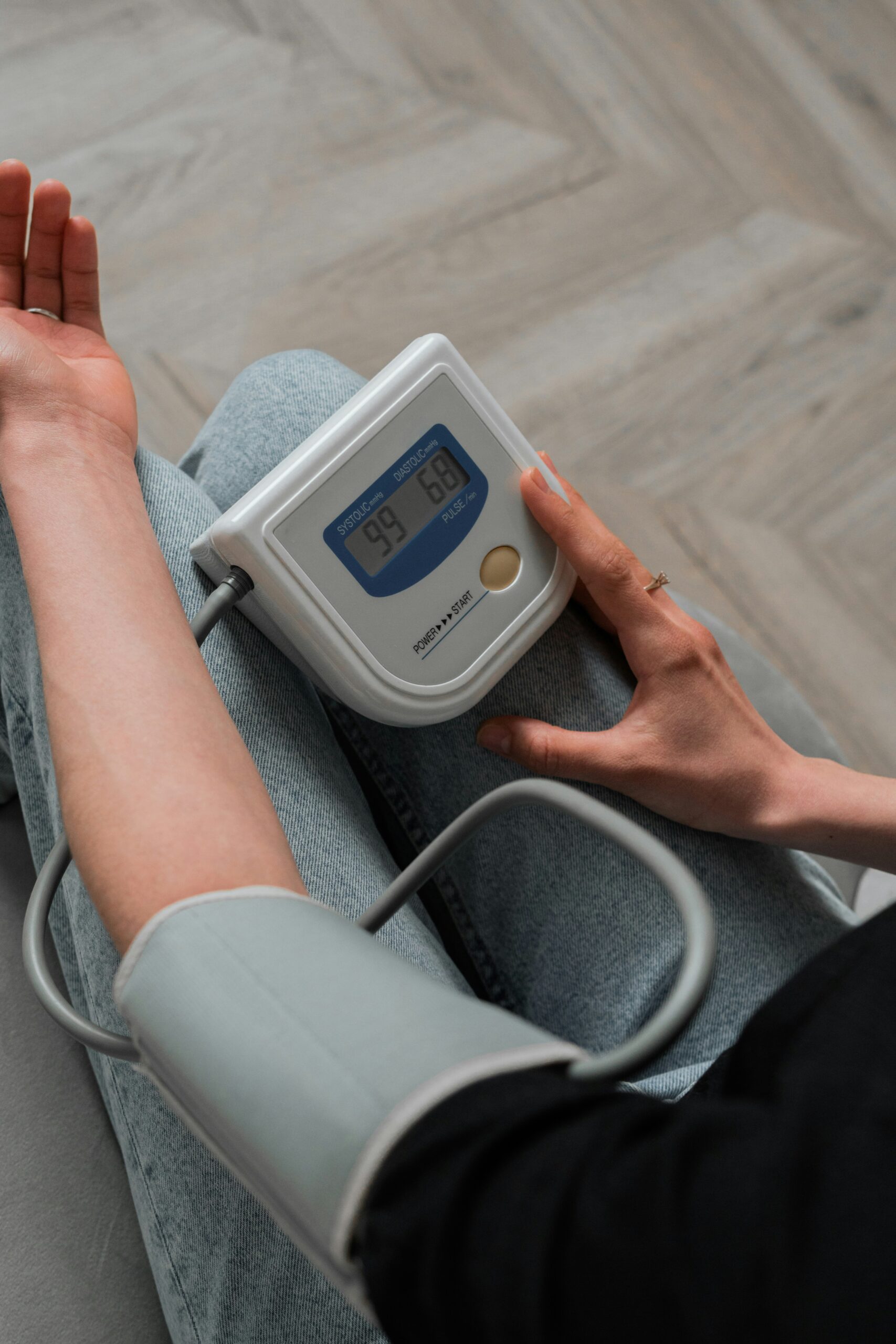
Regular blood pressure monitoring is essential for managing hypertension. Many people with blood pressure use home blood pressure monitors to check their readings regularly. Tracking your blood pressure at home can help you and your doctor determine how well your treatment plan works.
If your blood pressure readings remain elevated despite lifestyle changes and medications, your healthcare provider may need to adjust your treatment plan. Regular follow-up visits will help ensure you are on the right path toward controlling your blood pressure.
Managing hypertension is essential for protecting your heart and overall health. You can effectively control high blood pressure by adopting a healthy diet, staying physically active, managing stress, and following your healthcare provider’s advice. While medications may be necessary for some individuals, lifestyle changes play a key role in preventing and controlling hypertension. Regular monitoring and consistent efforts can help you maintain healthy blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. If you are struggling to manage hypertension, talk to your healthcare provider about creating a personalized plan that fits your needs and lifestyle.